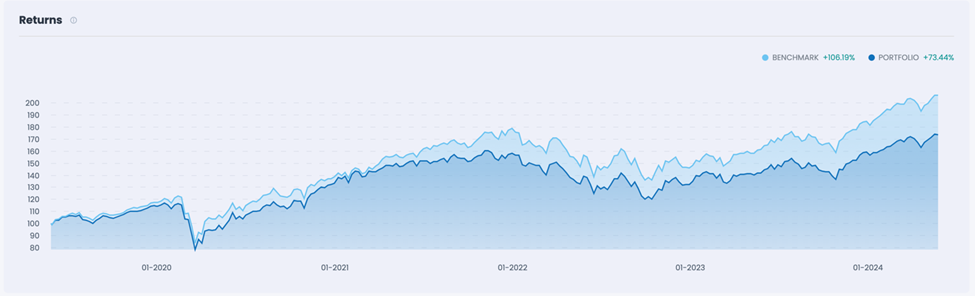
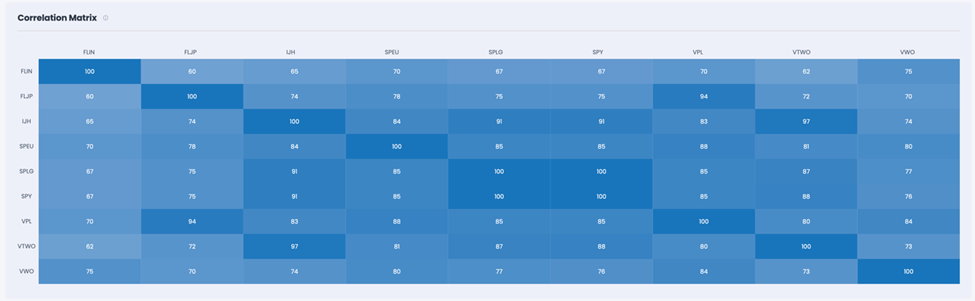
As financial advisors, it’s crucial to craft portfolios that maximize returns while minimizing risks. One effective strategy is diversification within the equity market using Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). This article explores how to achieve diversification beyond traditional large-cap indexes like the S&P 500, Russell 1000, and Russell 3000, which offer limited diversification power due to high correlations.
Understanding the Limitations of Traditional Indexes
Market-weighted large and mid-cap indexes (such as the S&P 500, Russell 1000, and Russell 3000) are often the cornerstone of equity portfolios. However, their high correlations (+98%) with each other reduce their diversification benefits. Additionally, these indexes have substantial exposure to mega-cap stocks, which can dominate portfolio performance:
| Company | S&P 500 | Russell 1000 | Russell 3000 |
| Microsoft | 7.14% | 6.29% | 6.00% |
| Apple | 6.10% | 5.39% | 5.10% |
| NVIDIA | 5.77% | 4.45% | 4.20% |
| Amazon | 3.72% | 3.42% | 3.20% |
| 4.20% | 3.90% | 3.70% | |
| META | 2.30% | 2.10% | 2.00% |
| Total | 29.23% | 25.55% | 24.20% |
With nearly a quarter of the portfolio tied to just a few companies, the diversification power of these indexes is further compromised.
Alternative Diversification Strategies
To achieve better diversification, consider incorporating mid-cap, small-cap, and international ETFs, which exhibit lower correlations with the S&P 500 and a lower concentration in the top positions.
Diversifying with Mid-Cap and Small-Cap ETFs
Mid-cap and small-cap ETFs provide exposure to a broader range of companies, reducing the dominance of mega-caps in your portfolio:
• Mid Cap (IJH): Correlation with S&P 500 is 91%
• Russell 2000 (VTWO): Correlation with S&P 500 is 88%
Adding International Exposure
International stocks offer a significant diversification benefit, with correlations to the S&P 500 below 85%:
• Europe (SPEU): Correlation with S&P 500 is 85%
• Japan (FLJP): Correlation with S&P 500 is 75%
• Asia Pacific (VPL): Correlation with S&P 500 is 85%
• Emerging Markets (VWO): Correlation with S&P 500 is 76%
• China (FLCH): Correlation with S&P 500 is 51%
• India (FLIN): Correlation with S&P 500 is 67%
Building a Balanced Equity Portfolio
To create a balanced equity portfolio, we recommend the following allocation. This strategy aims to achieve attractive returns while minimizing the risks associated with market dynamics and mega-cap dominance:
| ETF Used | Weight Top 10 | Correlation (SPY) | Proposed Portfolio Investment | 5-Yr Returns |
| SPLG (S&P 500) | 33.8% | 100 | 40% | $40,000 |
| IJH (Mid Cap) | 7.1% | 91 | 10% | $10,000 |
| VTWO (Russell 2000) | 6.8% | 88 | 10% | $10,000 |
| SPEU (Europe) | 19.5% | 85 | 12% | $12,000 |
| FLJP (Japan) | 23.5% | 75 | 7% | $7,000 |
| VPL (Asia Pacific) | 17.2% | 85 | 7% | $7,000 |
| VWO (Emerging Markets) | 20.0% | 76 | 10% | $10,000 |
| FLIN (India) | 30.9% | 67 | 4% | $4,000 |
This portfolio reduces exposure to top positions to 13.73% while providing exposure to over 5,000 stocks. The overall correlation with the S&P 500 is lowered to 90%, ensuring better diversification.
Conclusion
Diversification within the equity market using ETFs is an effective strategy to manage risks and enhance returns. By strategically allocating to mid-cap, small-cap, and international ETFs, financial advisors can create more resilient portfolios. This approach not only reduces over-reliance on mega-cap stocks but also provides broader market exposure, helping to protect against potential shifts in market dynamics.
We used CITEC AI platform to select, compare, analyze, and backtesting potential strategies.
Exhibit 1: POSITIONS
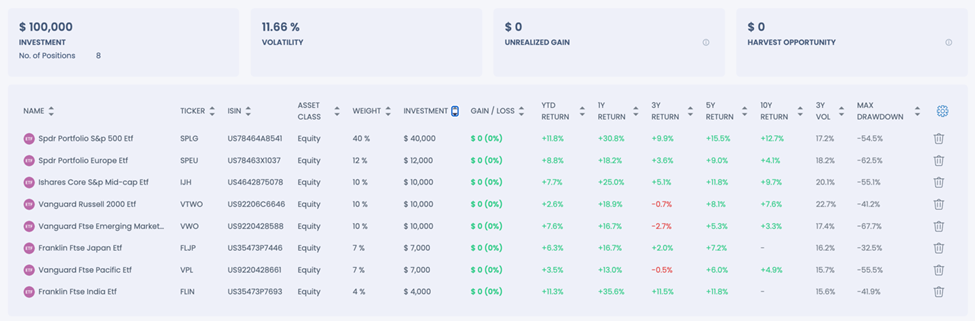
Exhibit 2: OVERVIEW
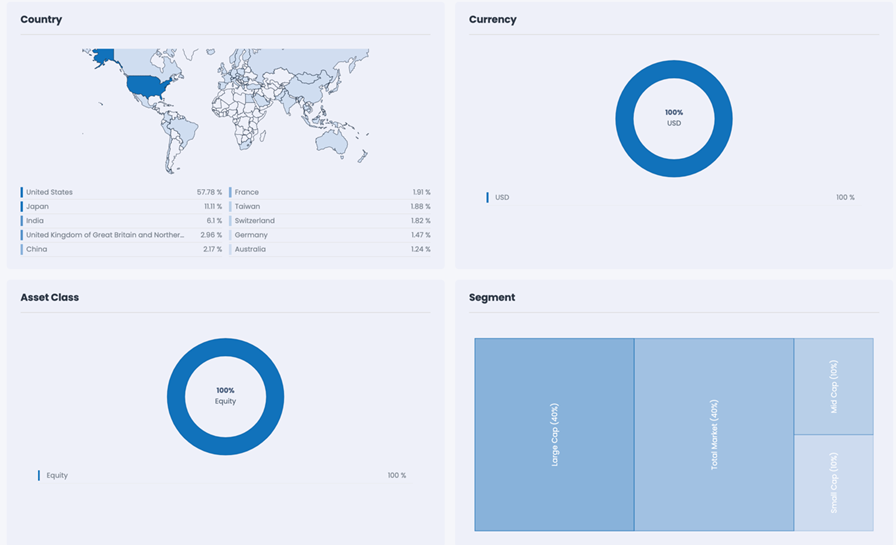
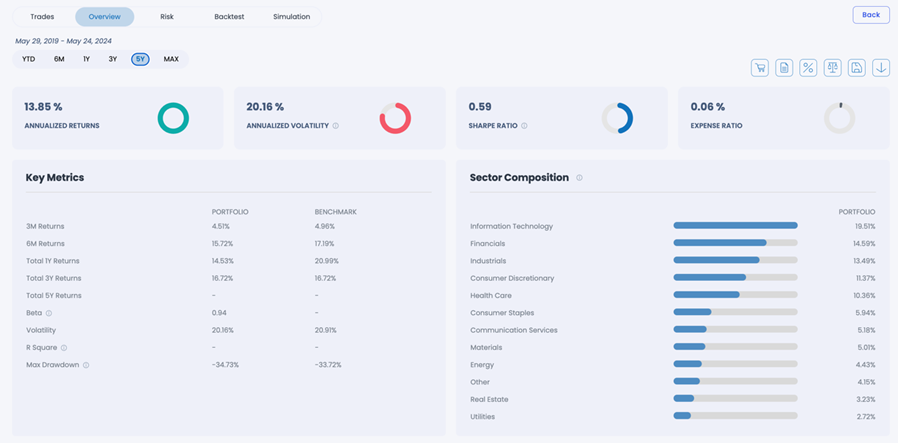
Exhibit 3: RISK
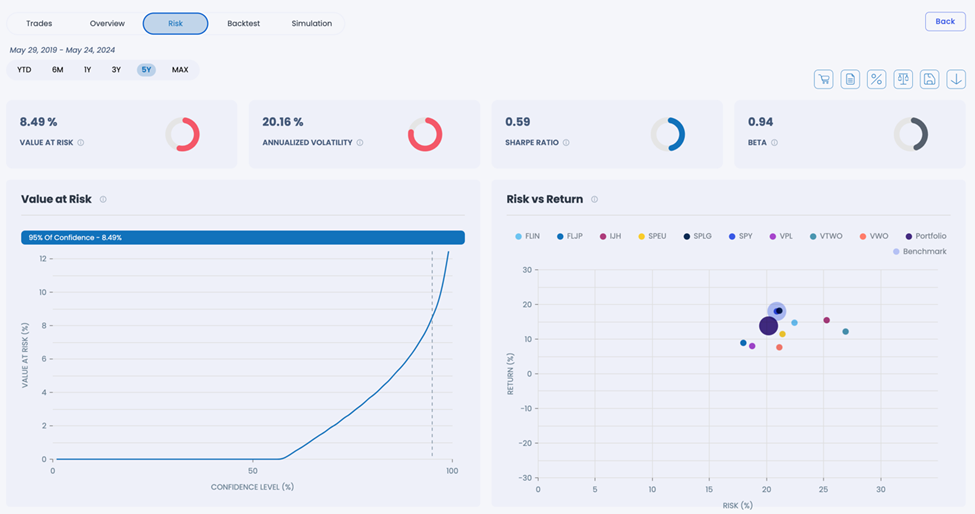
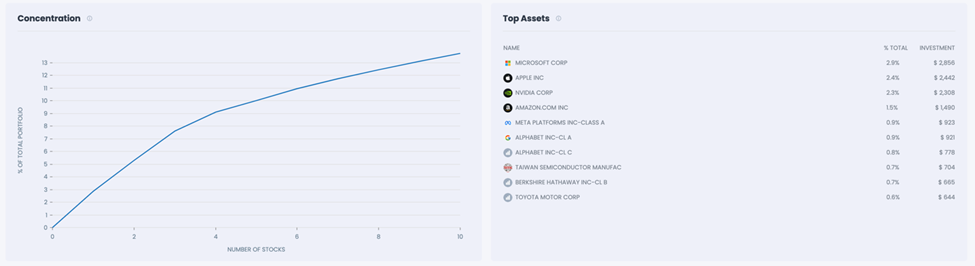
Exhibit 4: CORRELATION AND RETURNS